OUR SERVICES
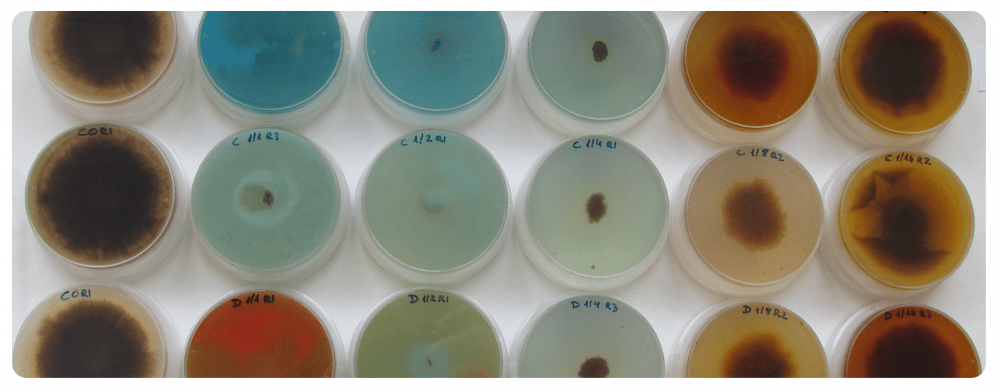
IN VITRO ACTIVITY ASSAYS
Antimicrobial activity of active ingredients, microbial strains or natural extracts can be evaluated against several plant pathogenic bacteria (including quarantine pathogens such us Xylella fastidiosa) and fungi. Different assay configurations, based in growth inhibition (agar incorporation or liquid test), or microbiocidal activity (contact test), can be performed. Dose-response titration assays can be done, and minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC), median effective dose (ED50), minimal bactericidal concentration or median lethal dose (LD50) can be determined, using conventional methods or a high-throughput platform with automatic microbiological analyzers.
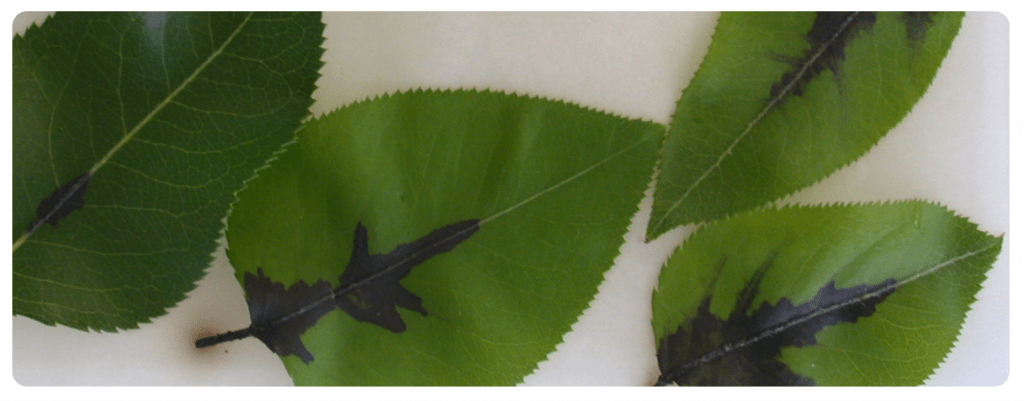

EX VIVO ASSAYS
This type of assays permit to screen the efficacy of the active ingredients, microbial strains or extracts under conditions in which the product, pathogen and host interact in high controlled pathosystem. Compounds are applied to detached plant organs (flowers, fruits, leaves, roots) either intact or previously wounded, and subsequently the pathogen is inoculated (postinfection/curative approach). The pathogen can be also inoculated simultaneously or before the treatment (preventative). The plant organ is then incubated in phytotron chambers under controlled environment conditions, for disease development. Several pathogens are available on demand, including bacterial and fungal, and aerial or root or fruit pathogens.

EFFICACY TESTING IN POTTED PLANTS UNDER CONTROLLED ENVIRONMENT CONDITIONS
The efficacy of control of bactericides or fungicides (also nematicides) can be assessed using whole-plant infection assays in a large variety of plants (Prunus, Pear, Apple, Quince, Olive, Grapevine, Pepper, Tomato, Strawberry, Rice, Pistachio…) under controlled greenhouse conditions (or Phytotron). For disease control, treatments can be applied using preventative (before pathogen inoculation), curative (after pathogen inoculation) or a combination of preventive/curative strategies, applied to plants by spraying, irrigation or microinjection to the trunk. Plants are cultivated under fully controlled day-night temperature cycles, relative humidity and light photoperiod, in the greenhouse. Disease intensity is determined as incidence or severity of infections.
